Edward Hood, HH Angus’ Medical Gas Specialist, recently joined an expert panel discussing the issues around medical O2 in the fight against the COVID-19 pandemic. Here is a summary of his presentation for the Canadian Healthcare Engineering Society webinar:
Challenges of increasing the numbers of oxygen outlets to an existing system with a fixed supply pipe size
Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, hospitals have experienced extraordinary increases in oxygen consumption due to high numbers of patients admitted to intensive care units. A complicating factor in their care has been the challenge of adding oxygen outlets to an existing zone for the purpose of treating COVID patients. Why is this a challenge? Simply put, many existing oxygen zones within a healthcare facility were not sized for large increases in oxygen flow. Many older healthcare facilities had their oxygen zones sized on oxygen outlet counts, which applied a diversity factor. That approach changed in the last few editions of CSA Z7396.1, which now focuses on understanding specific high demand zones (critical care for example), and designing robustly-sized piping infrastructure to those zones. However, the outcome is the same – many existing oxygen zones were never designed for “overflow” condition; as such, loading up existing oxygen zones by adding outlets or high flow oxygen devices must be managed very carefully.
Why is that? Substantially increasing oxygen flow in an existing oxygen zone will introduce increased pipeline pressure drops in the zone. A drop to 40 PSI at a zone valve will normally trigger the low alarm at the zone valve.
For this reason, it is important to analyze anticipated flow demand within the zone with the size of the oxygen service available in order to manage acceptable pressure losses that will not trigger alarm conditions.
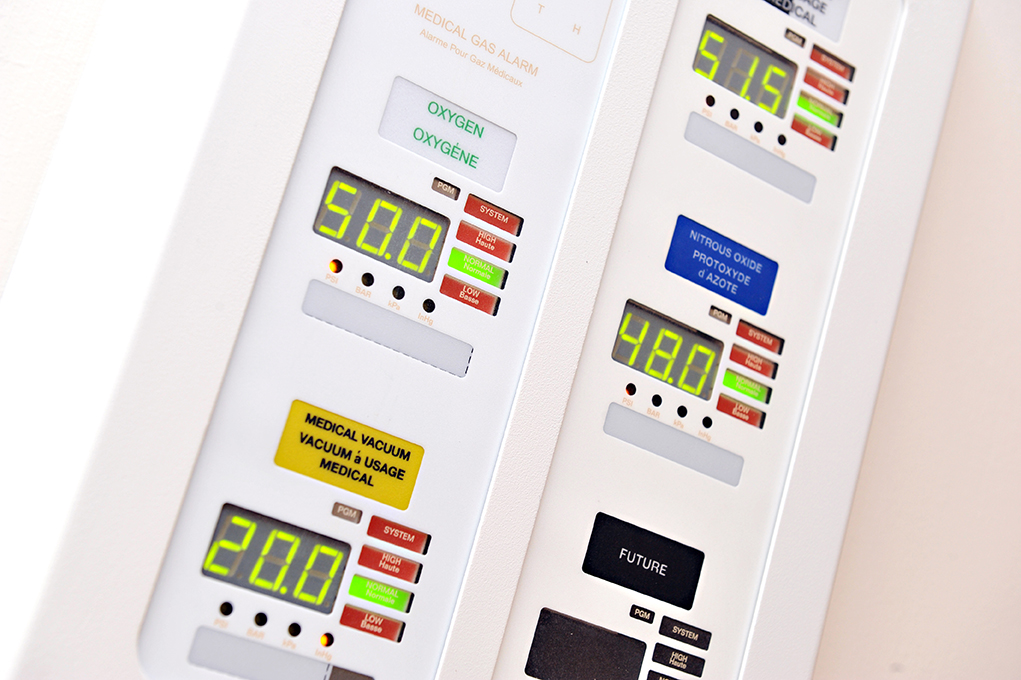

Factors affecting how many COVID patients can be treated in an existing medical gas zone
In hospitals, typical patient room usage is 5 L/min of oxygen; however, oxygen usage for COVID-19 patients can be up to 60 L/min or possibly higher, depending on the types of high flow oxygen devices in use. In order to manage pressure drops within a zone and avoid low pressure alarms, table E.5 in CSA Z7396.1 provides some guidance regarding expected pressure drops per 100ft of copper piping for a given pipe size. These pipeline pressure drops are:
- ½ inch pipe @ 190 L/min will have .5 pressure drop per 100ft
- ¾ inch pipe @ 500 L/min will have .5 pressure drop per 100ft
- 1 inch pipe @ 1000 L/min will have .5 pressure drop per 100ft
- 1 ¼ inch pipe @ 1800 L/min will have .5 pressure drop per 100ft
In other words, the following occupancy adjustments should be considered:
- ½ inch pipe
Non-COVID use = 38 patients in a zone
COVID use = 3 patients in a zone - ¾ inch pipe
Non-COVID use = 100 patients in a zone
COVID use = 8 patients in a zone - 1 inch pipe
Non-COVID use = 200 patients in a zone
COVID use = 16 patients in a zone - 1 ¼ inch pipe
Non-COVID use = 360 patients in a zone
COVID use = 30 patients in a zone
Concluding recommendations for ensuring adequate oxygen supply
- Before admitting COVID patients to a typical patient room, facility staff need to check the zone valve to verify pipe size in order to determine occupancy limits. Larger-sized zone valves are typically an indicator of a zone having greater capacity to flow oxygen with lesser pressure drops.
- Have a pandemic plan to identify where best to convert existing beds to COVID rooms. Consider the size of the oxygen zone valve serving the zone.
- If you are designing for a new hospital, consider designing a pandemic floor with medical gas pipelines capable of the worst-case scenario load, and consider the pressure drops from the bulk pad/source equipment to the zone in order to keep pressure drop for the pipeline to below 5 PSI per CSA Z7396.1 requirements.

Edward Hood, P.Eng., B. Eng.
Technical Leader and Senior Mechanical Engineer
edward.hood@hhangus.com